Childhood Amnesia
By the age of 7, we’ve forgotten more than half of our memories from early childhood.


By the age of 7, we’ve forgotten more than half of our memories from early childhood.

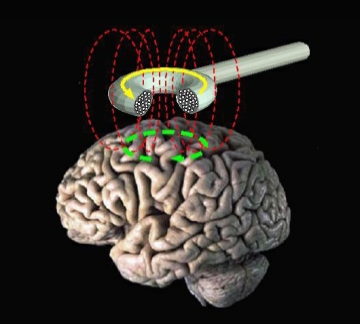
An experimental treatment for bulimia nervosa may help restore connections within the brain that influence eating behavior in some patients.

Trained musicians are better at distinguishing between their senses than the average person.


Eight years later, a population of Seattle crows still holds a grudge against the face of their human capturer.


Some people argue that food dyes are harmful to human health, but do decades of safety research back up these allegations?
Gluten-free diets are all the rage, but only a small portion of the population is truly sensitive to the wheat protein.

A common drug reverses social deficits and repetitive behaviors in mice with autism-like symptoms.

YOUNG BRAINS - Just how long does the teenage brain take to mature? How teenagers with autism see things differently. And, scientists reverse autistic-like symptoms in adolescent mice. Also: can you put barcodes on brain cells? And, what casino rats can tell us about gambling addiction.

Autistic teens and infants at risk for autism share a heightened interest in looking at objects.


Miniature “casinos” built specially for rats are helping researchers understand gambling addiction in humans.


ANIMAL & HUMAN HEALTH - A special report on the relationship between animal and human health, from pet obesity to cancer in tigers. Also, why spiders have prompted a massive Toyota recall. And, a citizen science project that’s pretty batty.

The Zoobiquity project teams up physicians with veterinarians to study diseases that affect humans and other animals.
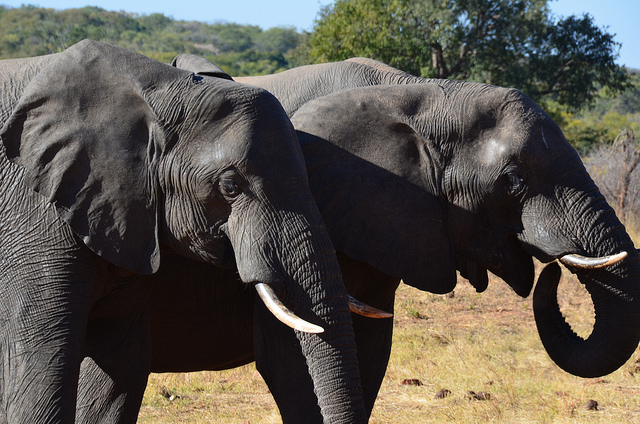

Elephants, unlike mammals much more similar to us, seem to instinctively understand pointing gestures.

PSYCHOLOGY & MEDICINE - Can literary fiction influence social astuteness? Why some people still fall for email spam. And, how sluggers' eyes can track fastballs in time to hit them. Also, how cell phones are transforming rural medicine.
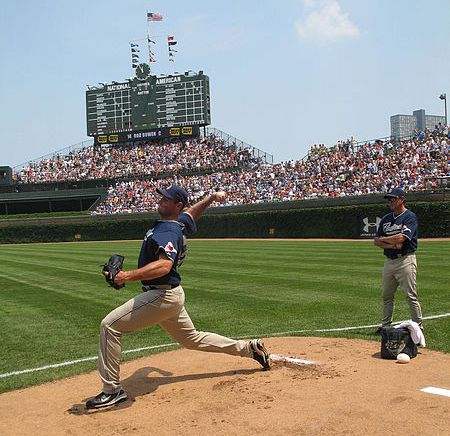

To hit a fastball, a batter's brain has to predict when it'll come across the plate.
