Ice Melt & Ice Age
A meltdown of Arctic ice may have triggered the last deep freeze in the Northern Hemisphere.

A meltdown of Arctic ice may have triggered the last deep freeze in the Northern Hemisphere.
No one likes having mucus, but in some circumstances, it may be able to fight dangerous bacteria.

Researchers think they’re found the cause of hypersomnia, a condition which causes people to feel constantly sedated.

In an upcoming case, the U.S. Supreme Court will consider whether diagnostic genes for breast cancer can be patented.

Scientists have isolated a potent painkiller from the venom of the deadly black mamba snake.
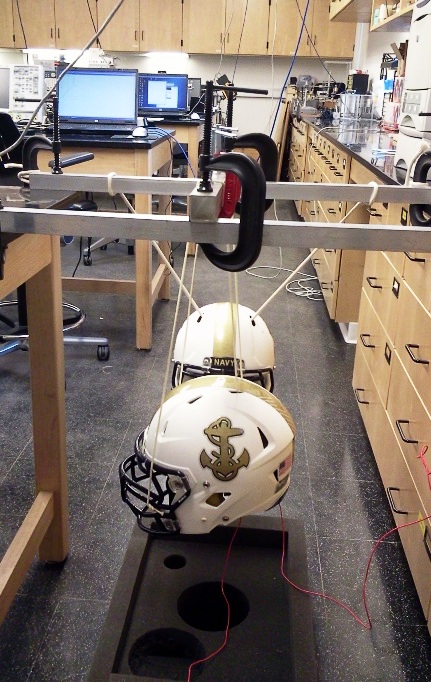

Measuring the acoustical signatures of colliding football helmets could help improve helmet safety.

BIRDS, BUTTERFLIES & BEETLES - How radar helped solve a migration mystery, why malaria could be heading north, and how dung beetles cool themselves off. Also: a 21st century technology that's helping archaeologists crack an ancient code.

Smoking while pregnant may cause DNA damage not just to the developing baby, but to that baby's future children.

Cells from amniotic fluid can be reprogrammed more stably than traditional stem cells.

MEDICAL INNOVATION - Medical implants that just melt away, how cancer research could make the plastics industry less dependent on fossil fuels, and why ultraviolet light is cleaning up hospital rooms. Also: scientists find a surprising new source of re-programmable cells in amniotic fluid. And a new genetic test that could help babies in the neonatal intensive care unit.

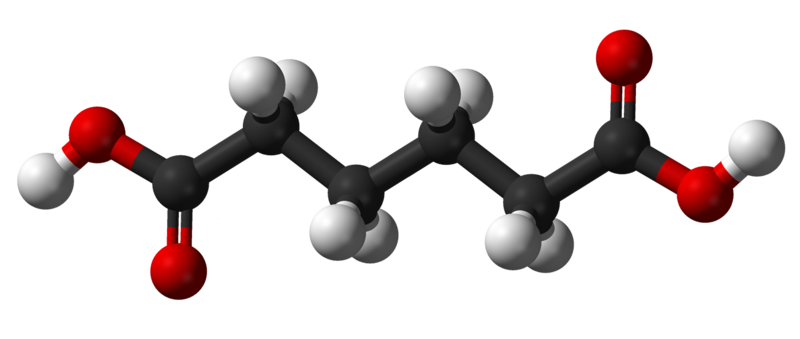
Researchers are developing temporary electronic implants that can be absorbed by the body.


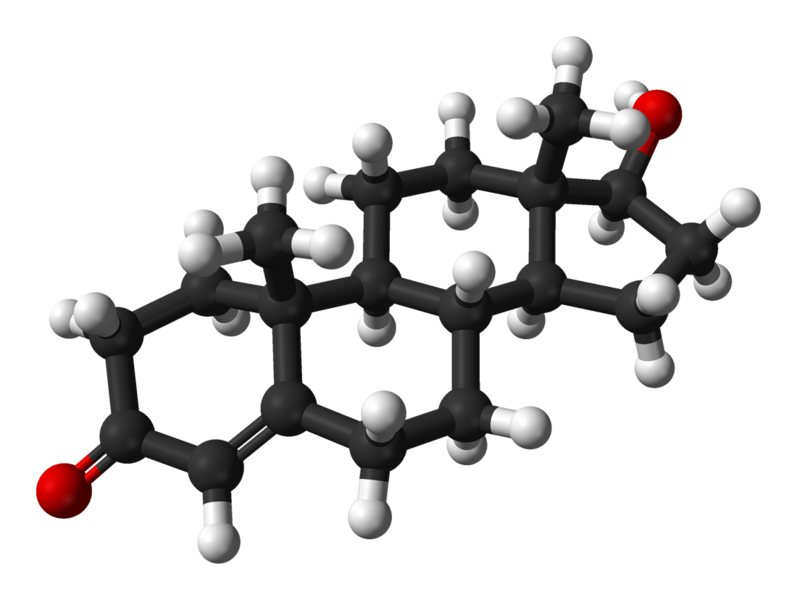
Over several centuries in Imperial Korea, eunuchs far outlived their non-castrated counterparts.

WEIRD SCIENCE: Listen to an archival podcast that delves into the weird and wacky side of science: Behind the legend of the chupacabra, does cracking your knuckles cause arthritis? A physiological explanation for near-death experiences, and animals that live without oxygen.
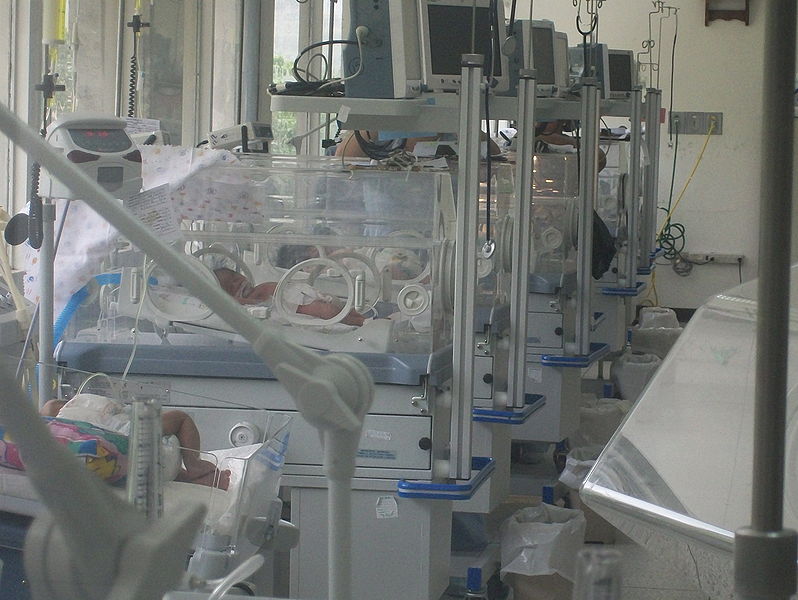
A new technique makes it possible to scan a sick newborn's entire genetic code in 50 hours.

It was once thought that mammals can’t regenerate tissue in the same way that some reptiles do. But new research suggests this might not entirely be the case.
