Oxygen-Deprived Mole-rats
An odd-looking little mammal uses a trick from the plant kingdom to survive without oxygen.


An odd-looking little mammal uses a trick from the plant kingdom to survive without oxygen.

Scientists are learning from birds’ amazing metabolisms to help human athletes perform better on the ground.

Researchers turn to panels of taste testers to identify key flavor chemicals lost during the past 100 years of commercial tomato breeding.
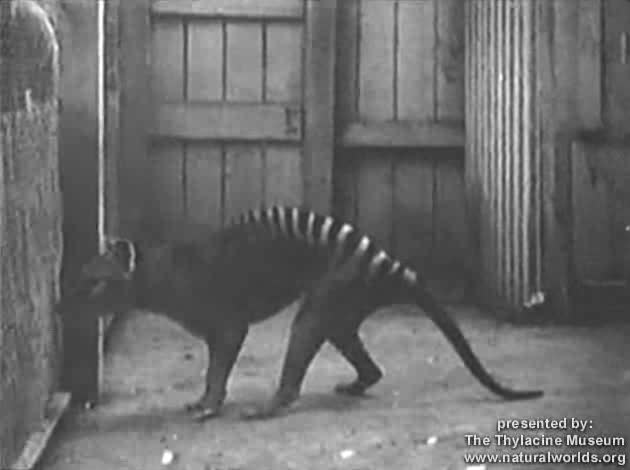

Scientists scanned preserved brains of extinct Tasmanian tigers in an attempt to better understand their behavior and life history.

Camels seem perfectly suited to life in the desert, but they may have evolved those traits in the high Arctic.

A listener asks whether it's true that large dogs don't live as long as small dogs.

Researchers develop the first fast-acting antidote for carbon monoxide poisoning.


Could teenage binge drinking have effects on the next generation, even if they’re never exposed to alcohol?
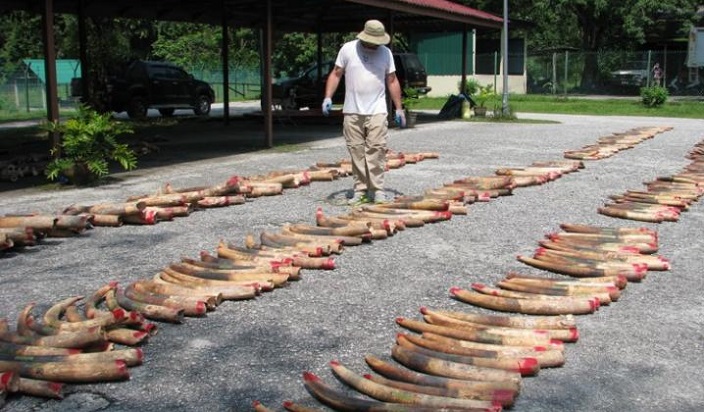

Chemical analysis of poached ivory reveals that elephant slaughter is massive and recent.

Researchers discover that the DNA mutations by which smoking causes cancer are more complicated than previously thought.
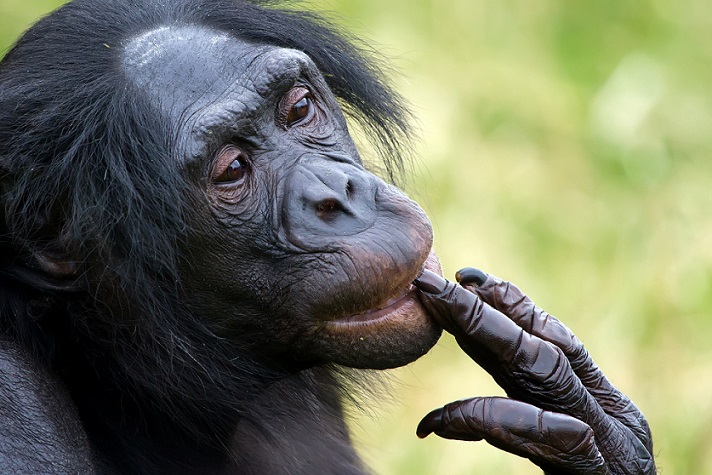

Even though the Congo River keeps them apart today, chimpanzees and bonobos managed to interbreed several times in the past.
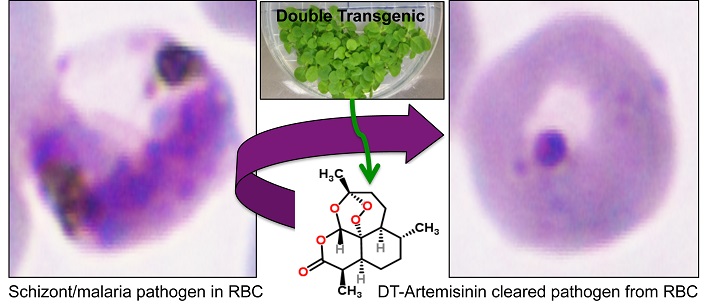
Genetically engineered tobacco plants produce potent artemisinin - a highly effective malaria drug - at a fraction of the usual cost.
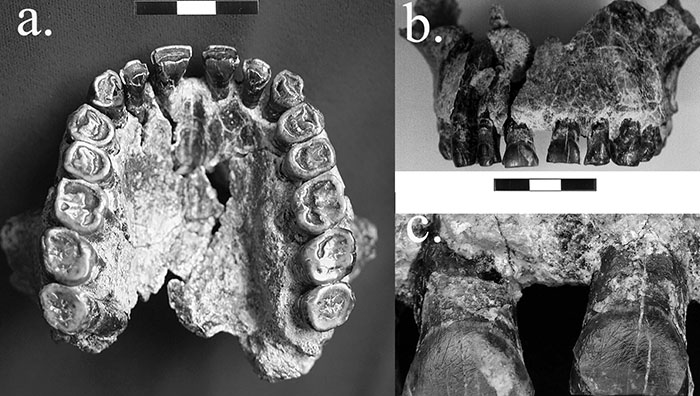
Analysis of a nearly two million-year-old jaw fossil from east Africa reveals clues to the evolution of the human brain.
Scientists use a powerful new gene editing tool to treat sickle cell disease.
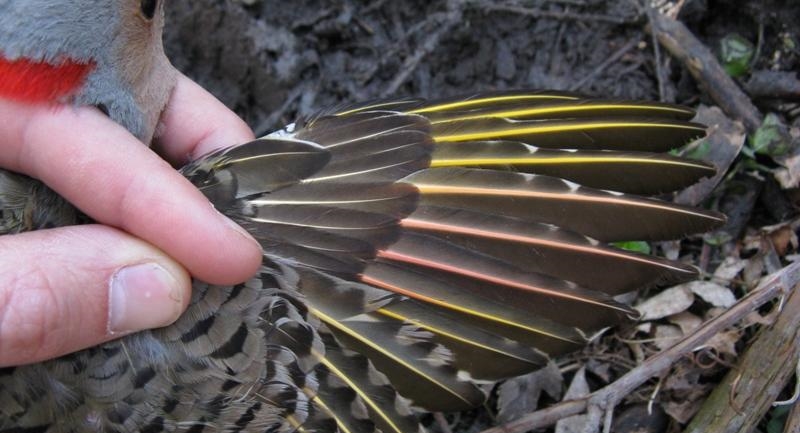

The berries of invasive honeysuckle plants are causing birds in eastern North America to change color.
Across the globe, humans have selected pigs with genetic mutations for black coats.


A DNA analysis reveals that giraffes make up four different species instead of just one.

New strains of lab mice are helping scientists understand complex disorders.

Scientists search for an arboreal African rodent that’s changed little in over thirty million years.

A random mutation allowed our ancestors to stay relatively healthy despite exposure to toxic woodfire smoke.
